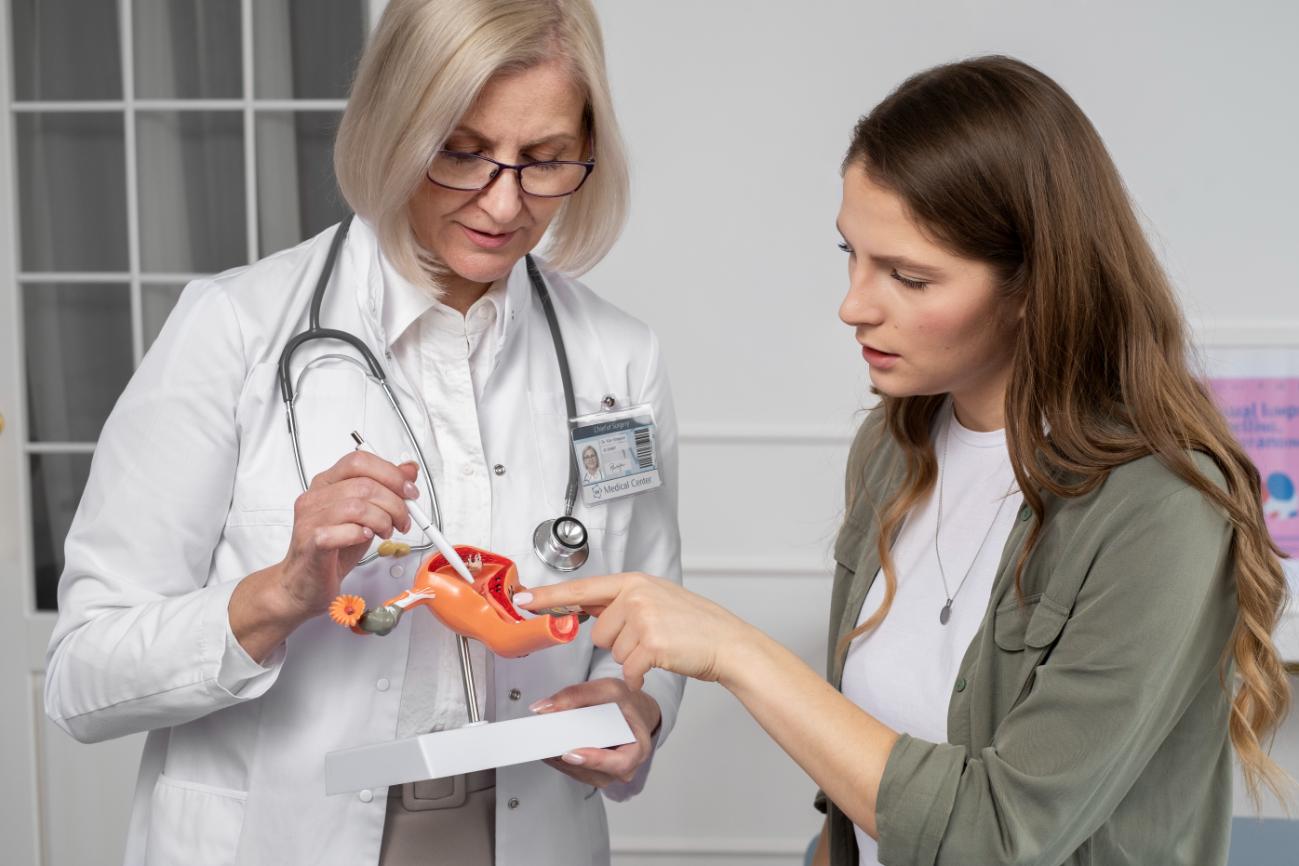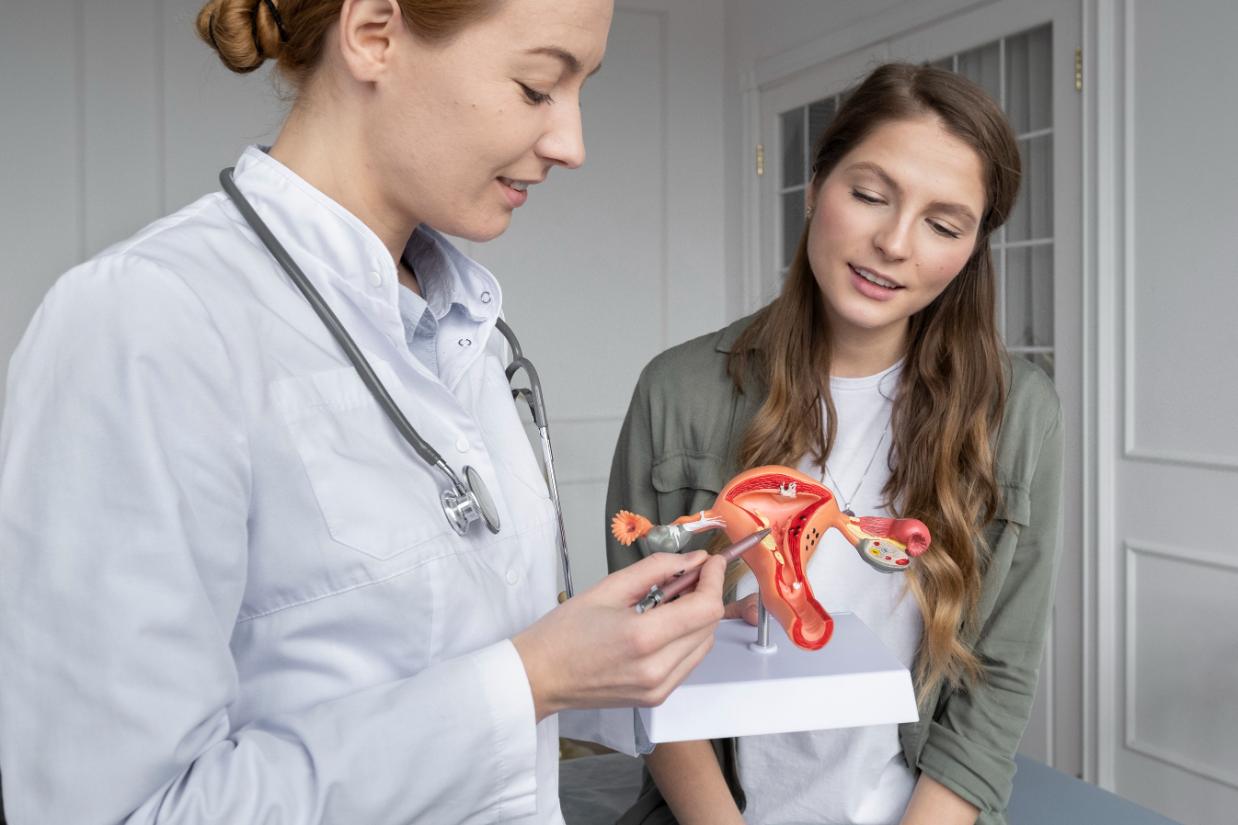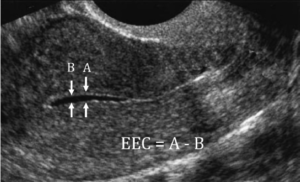
The uterus, which carries the fetus in females throughout the pregnancy, consists of three layers – inner most, middle and outer layer. The innermost layer of uterus is called endometrium. A thick and healthy endometrium is crucial for normal menstrual cycle and trouble-free pregnancy. Endometrium is also known as uterine lining. Thick endometrium also goes a long way in ensuring effective implantation of fertilized eggs inside uterus. Uterine Lining must be at least 8 mm thick for successful implantation of fetus. Later, during the pregnancy, it also nurtures the fetus, enabling it to grow. If the endometrial lining is thin, implantation will not take place, resulting in failure of pregnancy
Two hormones produced from the ovaries thicken and prepare the uterine lining for implantation viz. estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen has a significant role to play in keeping the endometrium thick, salutary and blood-rich, whereas progesterone supplements in preparation for transfer of an embryo into the uterine cavity. Numerous medical studies have found that if a woman has persistently thin uterine lining, chance for pregnancy is less even if there is adequate estrogen. There are five main reasons for a thin endometrial lining.
[button title=”Talk with A Gynaecologist” link=”https://www.kjkhospital.com/contact-us/” target=”_blank” align=”” icon=”” icon_position=”” color=”Blue” font_color=”Red” size=”4″ full_width=”” class=”” download=”” onclick=””]
1. Low estrogen level:
Primary reason for a thin endometrial lining is lack of adequate estrogen. Your doctor can check if the estrogen level in your body is adequate with a blood test. If it is below the normal range, you can replenish your estrogen level in the form of tablets, injections or patches.
2. Damaged endometrial lining:
Having a thin endometrial lining despite the presence of adequate estrogen may be the result of a previous uterine infection which has damaged the uterine lining and caused the formation of scar tissue.
3. Decreased blood flow:
Though not a common cause of thin endometrium, insufficient blood flow to the endometrium may lead to thinning of the lining. Your doctor can check for this by way of ultrasound to measure blood flow to the uterus.
4. Uterine fibroids:
Uterine fibroids refer to benign growths that develop in the uterus. They can be either so small that they are unable to be seen by the human eye or large enough to cause bulges in the uterus.
5. Chronic endometritis:
Chronic endometritis refers to the infection of the endometrial cells, leading to inflammation of the uterine lining. It is not a life-threatening infection, still it is important to get it treated as soon as possible. Your doctor may prescribe a course of antibiotics. If it is at the chronic stage, you may need intravenous fluids and bed rest in a hospital.
In case of an in vitro fertilization, your doctor will check the health of your endometrial lining in order to ensure that you have the best chance of becoming pregnant.
Symptoms of thin endometrium:
- Issues pertaining to infertility
- Abnormal or irregular menstrual cycle
- Irregular or painful menses
- Inadequate menstrual bleeding
Treatment for thin endometrium:
Adequate endometrial thickening is a key factor for the embryo to adhere to the wall of the uterus and pregnancy. Though plenty of treatment modalities are there to improve the thickness of the uterine wall and the subsequent endometrial receptivity, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is considered to be the best treatment for endometrial thinning and scarring from miscarriages. It can be called an ovarian rejuvenation treatment that helps women fight low ovarian reserve. It is a novel gynecological approach and various studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of this technique.
PRP is autologous blood plasma that has been enriched with platelets at about 4-5 times more than the circulating blood. PRP can stimulate proliferation and regeneration with a large amount of growth factors and cytokines. PRP has been proven to aid endometrial growth and subsequently on the pregnancy rates as endometrial thickness is directly proportional to the uterine thickness. PRP treatment is particularly helpful in case of recurrent abortions owning to endometrial weakness, as it can stimulatethe development of new tissue, making the uterine lining grow thicker. PRP is a safe procedure, with minimal risks of transmission of infectious disease and immunological reactions since it is made from autologous blood samples.
Even if one undergoes assisted reproductive technology, thin endometrium is identified to negatively affect the reproductive success rate. Medical studies have demonstrated that PRP can increase the success rate of IVF treatments. It is believed that the failure of IVF treatments isn’t caused by the embryo, but the uterus.
Apart from gynecology, PRP treatment has been using in other medical fields like helping athletes recover from sports-related injuries, helping women overcome premature menopause, skin rejuvenation etc.
If women are grappling with issues related to pregnancy, like unable to get pregnant or difficulty in holding pregnancy, they must get their estrogen level and thickness of endometrium checked. It should be noted that with the advent of PRP, the possibility of achieving pregnancy with one’s own eggs has increased tremendously.
For questions related to the treatment of thin uterine lining, send a message to www.KJKHospital.com/contact