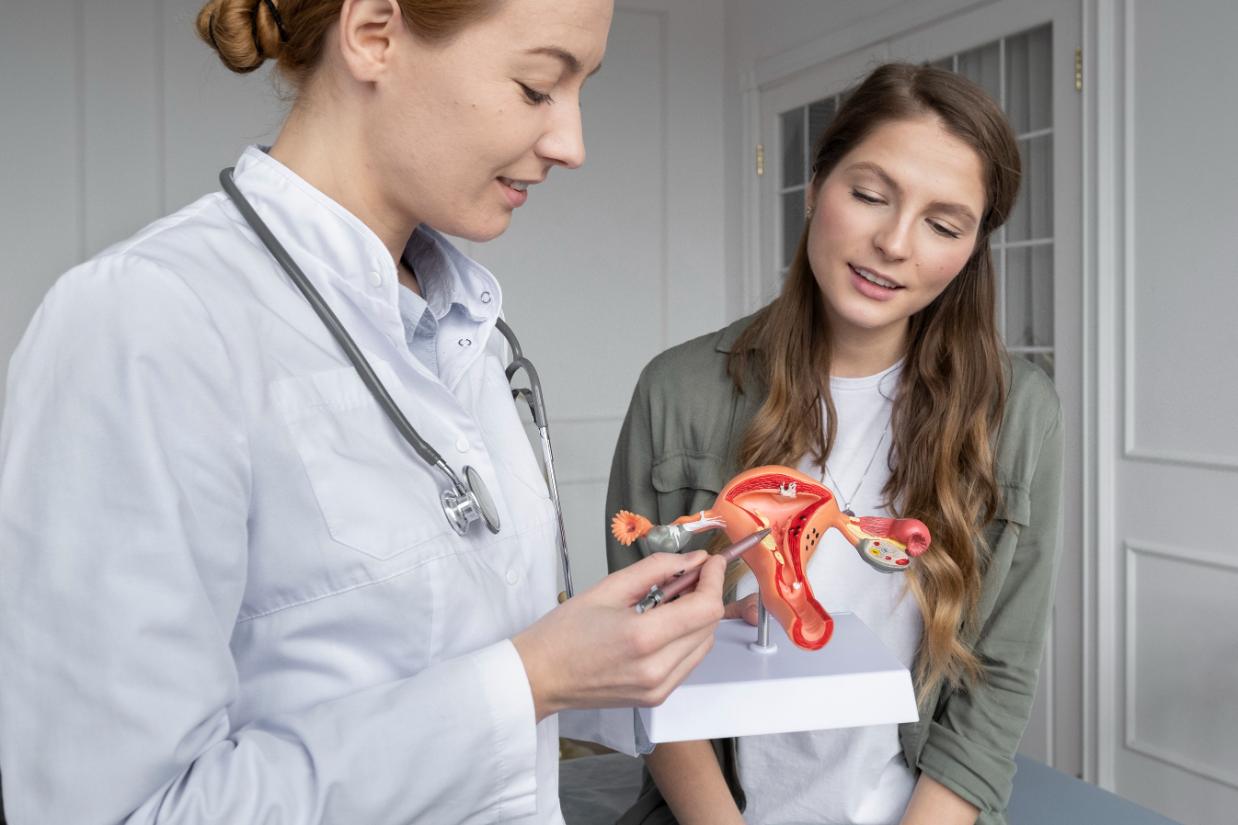
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous tumors that occur in the uterus, usually in the childbearing years. These tumors are formed from the muscle fibers that line the uterine wall, known as myometrium, and usually do not cause any pain, which is why they often go undiagnosed unless they any tests in the uterus are undertaken.
Fibroids appear in different sizes – from being small undetectable masses to huge masses, which can disturb the functioning of the uterus. These can also appear as singular or multiple. A large number of women have uterine fibroids at least once during their lifetime. But most of them go undetected as women in most cases do not exhibit any symptoms.
Common Types Of Fibroids
There are four types of uterine fibroids that occur, which are classified based on their location in the uterus.
- Intramural Fibroids
They are fibroids that grow within the muscular wall of one’s uterus and are the most common type. These are harmless if they are small in size, however, large ones may stretch and distort the uterine cavity, or the womb.
- Subserosal Fibroids
These fibroids are formed on the thin layer of tissue that envelops the uterus, called serosa. When the tumor grows outward, projected by a small tissue, while remaining attached to the surface of serosa, they are known as pedunculated fibroids.
- Submucosal Fibroids
These fibroids grow beneath the uterus muscle and may cause infertility or excessive bleeding. This type of fibroid occurs quite rarely.
- Cervical Fibroids
The Cervical Fibroids, as the name suggests, develop on the walls of the cervix, which is nothing but the neck of the uterus.
Causes Of Fibroids
Although it is not known what exactly causes fibroids, extensive research has listed the below as possible causes:
Hormonal imbalance
Progesterone and estrogen are hormones that help in regenerating the uterine wall during each menstrual cycle. Excess production of these hormones can cause the growth of fibroids.
Genetics
It is found that the chances of fibroids are increased significantly if any close relative (mother, sister, grandmother, aunt) in the family has a history of fibroid.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy causes an increase in the production of progesterone and estrogen in the body. As mentioned above, these excess hormones can result in the development of fibroids.
Symptoms Of Fibroids
In many of the cases, fibroids are asymptomatic, that is, they do not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, a woman may be having uterine fibroids if she has any of the below symptoms:
- Heavy bleeding during menstruation cycles.
- Dull pain in the pelvic region or the lower back area.
- Unusual cramping experienced during periods.
- Unusually long period cycle.
- Pain while having sexual intercourse.
- Unexplained swelling of the abdomen, and sudden weight gain.
Diagnosis Of Fibroids
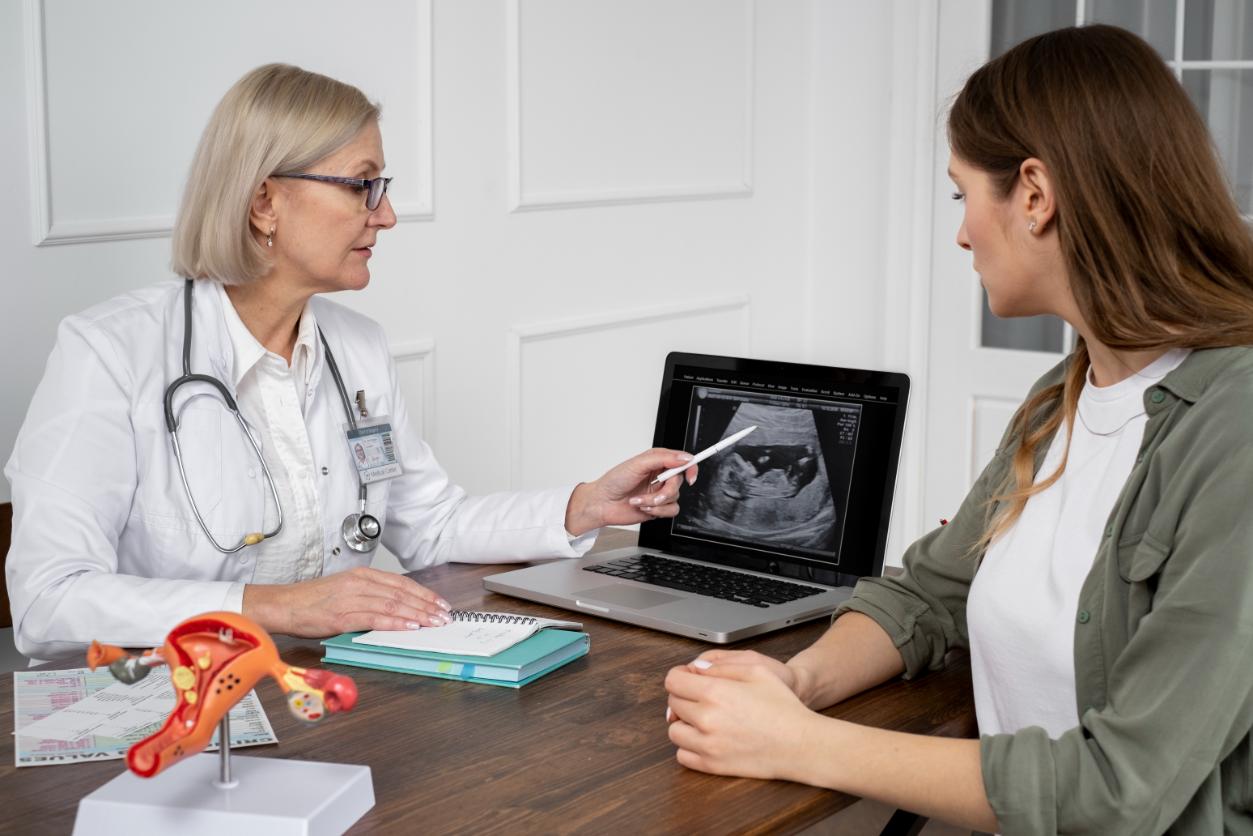
Fibroids are generally diagnosed by a pelvic exam, in which the condition, size, and shape of the uterus are examined. Apart from the pelvic exam, there are other means of tests that can indicate the presence of fibroids:
Ultrasound
In an ultrasound, high-frequency sound waves are used, which reproduce the images on a screen connected to the ultrasound wand. This helps the doctor to detect the presence of fibroids. A variation of this is the transvaginal ultrasound, which provides better images as the ultrasound wand is inserted into the vagina, as the vagina is much closer to the uterus.
Pelvic MRI
The pelvic MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan is similar to an MRI scan of any other part of the body and is used to get the images of the ovaries, uterus, and other such organs.
Saline Sonohysteragram
This is a type of vaginal ultrasound in which fluid (saline) is inserted into the uterus. The fluid expands the uterus, which helps detect the presence of fibroids.
Hysteroscopy
In Hysteroscopy, a surgical procedure is performed to directly view the presence of fibroids in the uterine cavity.
Treatment Of Fibroids
If fibroids are detected, the doctor begins the treatment. The treatment plan depends on age, size of the fibroids, and general health of the patient. Based on these, a combination of treatments may be suggested:
Treatment At Home
In some cases, the fibroids are of much smaller size that external medication is not necessary. In such cases, the patient can follow a few home remedies as listed below to reduce discomfort and improve overall health. These include:
- Acupuncture
- Yoga
- Body massage
- Heat pads for cramps and pain
- Changes in diet to include more low-calorie foods.
In certain women, fibroids may cause a rapid gain in weight. An active lifestyle helps monitor and manage weight and reduce the effects of fibroids.
Medications
Certain medications may be prescribed by doctors to control the level of hormones, and in turn, reduce the size of fibroids.
Medicines that contain ‘Gonadotropin-releasing hormone’ (GnRH), such as leuprolide or Lupron, help reduce estrogen and progesterone levels, which eventually reduce the size of fibroids.
Surgery
In severe cases, surgery can also be performed to remove very large or multiple growths of fibroids. This procedure is known as a myomectomy. But these have a temporary effect as fibroids often grow back after surgery.
In certain cases, a hysterectomy may be required if other treatment options do not work. In such a case, the patient will not be able to have kids.
Fibroids Treatment In The Long Term
As mentioned earlier, the treatment depends on the size and location of the fibroids. In most cases, fibroids may not need treatment, especially if they’re small or do not cause any symptoms.
The treatment options depend on the severity of the symptoms, and whether the patient wishes to bear children in the future or not. A gynecologist or obstetrician will provide the best guidance.
Despite the on-going research, it is still not known how to prevent the occurrence of fibroids. However, a healthy and active lifestyle by exercising and consuming high nutrition food can help in reducing the risk of fibroids. If you are diagnosed with fibroids, talk to your doctor to get the appropriate treatment.
For enquiries and online appointments, send a message to www.KJKHospital.com/contact