Overview
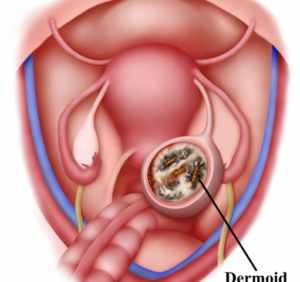
A dermoid cyst is a saclike growth that is present since birth. It is characterized by the presence of structures like hair, teeth, fluid, or skin glands that are found on or in the skin.
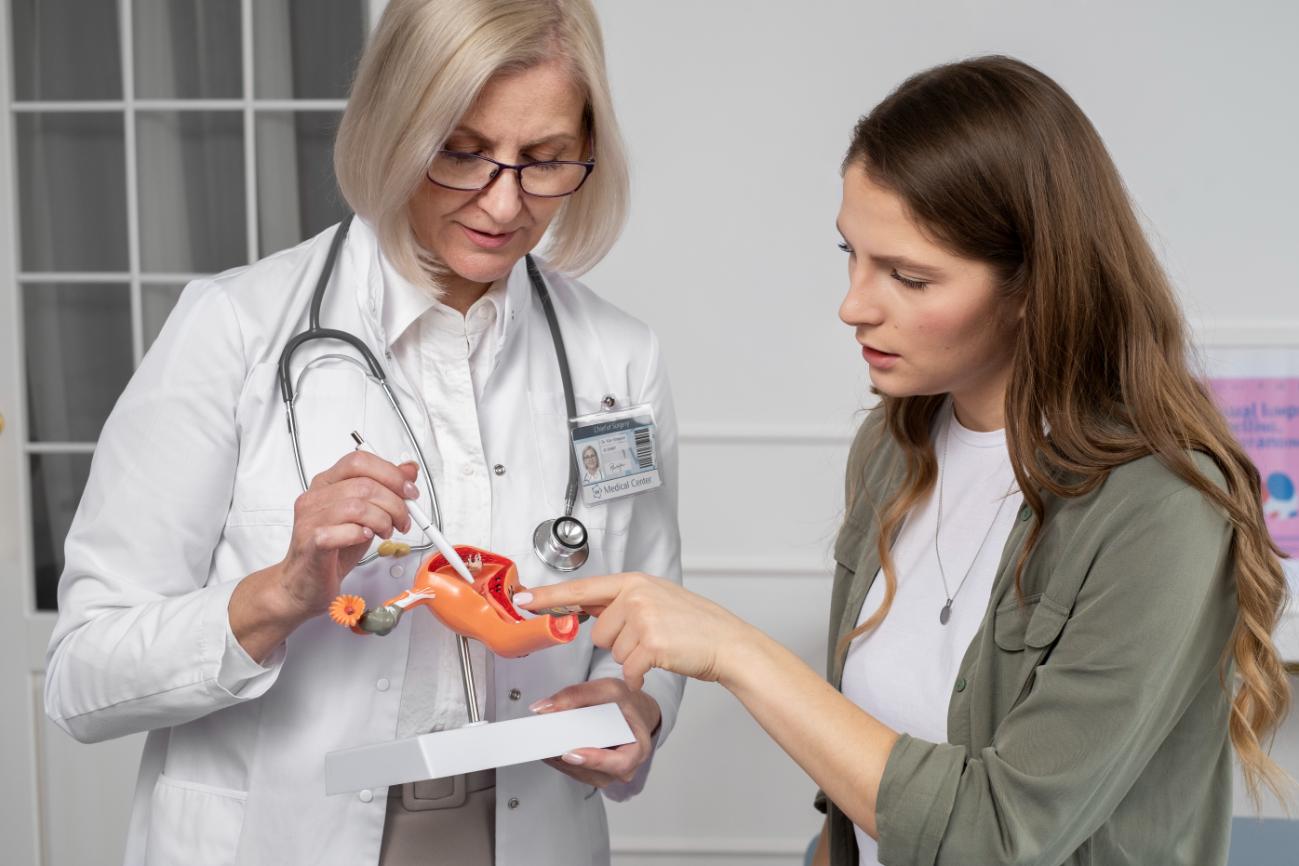
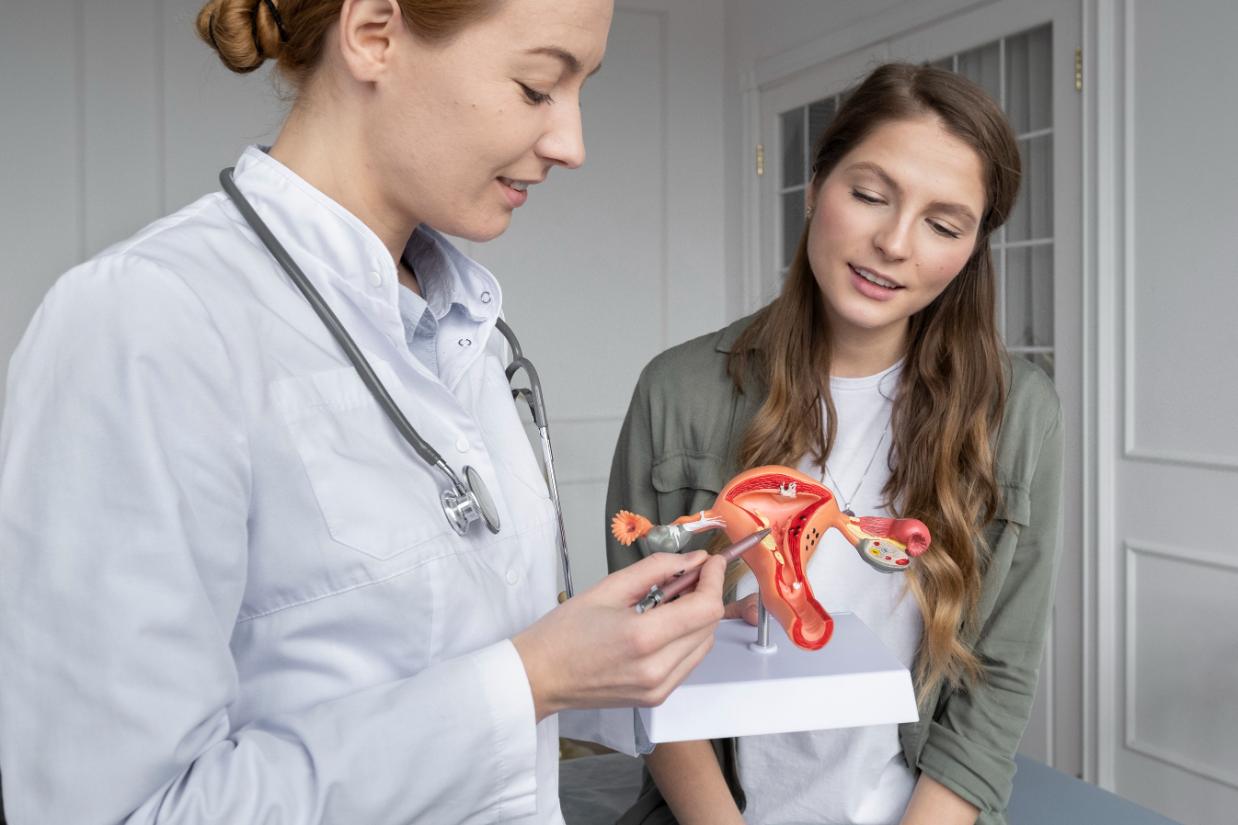
Ovarian dermoid cysts are a type of dermoid cyst. It develops from a totipotent germ cell (a primary oocyte) that grows all the three layers of tissue in the body; hence, they usually contain materials such as hair, teeth, fat, bone, cartilage, and, in some rare cases, even thyroid tissue. They are also called ovarian teratomas.
These cysts can occur at any age, but they are generally detected during the reproductive years. Most women who develop dermoid cysts on their ovaries are around 30 years of age. Up to 15% of women have dermoid cysts on both their ovaries. They vary in size, from a centimeter to 45 cm in diameter. Ovarian dermoid cysts are benign in 98% of the cases, but in the rare 2% of the cases, they can turn malignant. So regular follow-up is required.
Symptoms
Ovarian dermoid cysts usually cause no symptoms, except when they become fairly big in size, causing pressure on the surrounding areas. The symptoms caused by these large dermoid cysts include:
- Abdominal pain
- Abnormal bleeding
- Painful sexual intercourse
- Nausea and vomiting
- Painful urination or difficulty in emptying the bladder
- Weight changes
Complications
One of the most common and biggest complications with the ovarian dermoid cyst is ovarian torsion. When an ovarian dermoid cyst becomes too big, it rotates on its axis, thereby causing torsion of the ovary. This can go undetected for some time, and if it stays like that for too long, it can lead to loss of an ovary. This is a surgical emergency and needs to be addressed immediately.
Diagnosis
Ovarian dermoid cysts usually remain undiagnosed due to being asymptomatic in nature. These are usually diagnosed by pelvic or transvaginal ultrasound. At times, Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) may be done to ascertain the exact number, size, and location of the cysts. Dermoid cysts in the ovary can be present bilaterally in both ovaries; so both ovaries should be checked.
Treatment
The treatment of dermoid cyst is aimed at removing the cyst without having to remove the ovary. This can be done laparoscopically or by traditional open laparotomy. This is called location cystectomy.
If the cyst becomes too big, the ovary is also removed with the cyst. This is called oophorectomy. This can also be performed laparoscopically or by an open laparotomy.
In the case of an ovarian torsion too the whole ovary has to be removed. It causes sharp, acute pain, which is a surgical emergency.
Ovarian cystectomy and oophorectomy are mostly performed laparoscopically, as it is a minimally invasive method and requires little to no hospital stay postoperatively.
Here’s where you can reach us for appointments or for answers to all your pregnancy related questions
http://www.kjkhospital.com/contact-us/
Phone Numbers: 0471-2544080, 2544706
Email: kjkqueries@gmail.com
Subscribe to KJK Hospital YouTube Channel and stay updated with the latest in Pregnancy and Infertility.
Subscribe Here –