Introduction
Gynecological cancers are cancers that start in a woman’s reproductive organs. The various types of gynecological cancers are named after the reproductive part, where it starts. Some women develop these cancers just before menopause. Menopause does not cause cancer but the risk of developing cancer increases with age.
Types
Various types of gynecological cancers are:
- Cervical cancer- It is the most common gynecological cancer worldwide.
- Ovarian cancer
- Vaginal cancer
- Vulvar cancer
- Uterine cancer
Symptoms
Different gynecological cancers have different symptoms, but some may be overlapping.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge is common to all gynecological cancers except vulvar cancer.
- Pelvic pain or pressure is commonly seen in ovarian and uterine cancer.
- More frequent or urgent needs to urinate and constipation are commonly seen in ovarian and vaginal cancer.
- Feeling full too quickly or having difficulty eating, bloating, and abdominal or back pain are seen only in ovarian cancer.
- Itching, burning, pain, or tenderness of the vulva and changes in the color or skin of the vulva such as rash, sores, or warts are only seen in vulvar cancer.
- One should consult a doctor in case of any of the above symptoms. Some of these symptoms are seen in conditions other than cancer also, and hence it has to be ruled out.
- Apart from the above symptoms, one should immediately consult their doctor if there is vaginal bleeding after menopause and if there is heavier than normal bleeding during periods or if the periods last longer than normal.
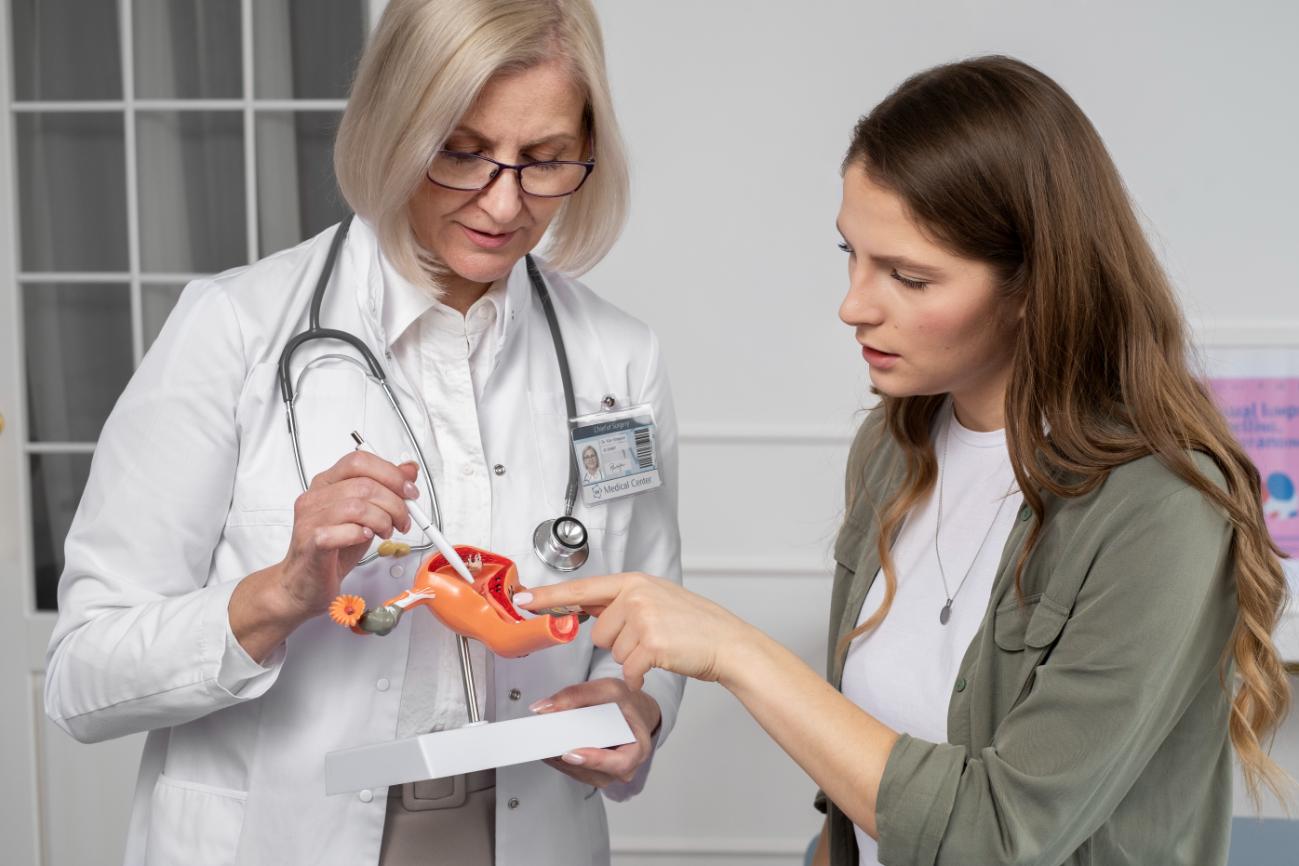
Diagnosis & Treatment
In the case of cervical cancer, there is an advantage of screening tests where individuals who undergo regular screening tests can detect cancer before any symptoms develop. This early detection can lead to a more effective treatment.
Pap and HPV tests are the screening tests available for cervical cancer. The Pap test also helps prevent cervical cancer by finding precancers, cell changes on the cervix that might become cervical cancer if they are not treated appropriately.
Diagnostic tests for gynecological cancers involve:
- Blood tests for various blood markers that are particular to some of the cancers like CA 125 for ovarian cancer.
- Diagnostic imaging tests like MRI, CT. They also detect if cancer has spread or metastasized to other parts of the body.
- Ultrasonography of the abdomen to detect the primary tumor.
- Tumor biopsy or Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) to differentiate between a benign and malignant tumor and to be able to classify and stage the tumor.
Treatment options for gynecological cancers are mainly 3 types:
- Surgery – Depending on the type and extent of cancer, surgery is the best and most preferred treatment. The entire tumor(cancer) and surrounding normal tissue are removed.
- Chemotherapy – In this line of treatment, special drugs that shrink or kill the cancer cells are given either orally or in the vein.
- Radiation therapy – A recommended dose of targeted high-energy radiation is given.
Surgery is mostly followed or preceded by chemotherapy or radiation. It depends on if the cancer is sensitive to chemotherapy drugs or radiation.
The HPV vaccine is recommended as a way to reduce an individual’s risk to develop cervical cancer.
Here’s where you can reach us for appointments or for answers to all your pregnancy related questions
http://www.kjkhospital.com/contact-us/
Phone Numbers: 0471-2544080, 2544706
Email: kjkqueries@gmail.com
Subscribe to KJK Hospital YouTube Channel and stay updated with the latest in Pregnancy and Infertility.
Subscribe Here –