IUI Treatment in Trivandrum, Kerala
Infertility does not always mean IVF. Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a type of fertility procedure in which the sperm that have been washed and concentrated are deposited directly into the uterus. It comes under the ambit of artificial insemination and is a very common procedure for treating infertility. Intrauterine insemination is also known as donor insemination, alternative insemination, or artificial insemination. The intention of this procedure is to get the healthy sperm closer to egg. This way the number of sperm cells reaching the fallopian tube can be increased, thereby increasing the chances of fertilization. This procedure can provide the much-needed head-start to the sperm, though it still requires sperm to reach and fertilize the egg, resulting in a normal pregnancy. Through intrauterine insemination, the sperm can swim into the fallopian tube without any obstacles. The principal advantage of this procedure is it is less expensive and less invasive compared to an in-vitro fertilization (IVF). Intrauterine insemination can be aligned with your normal cycle or with fertility-boosting medications. The way with which the insemination is coordinated depends on the reasons for infertility.
How does intrauterine insemination function?
As already mentioned, in intrauterine insemination sperm cells are put directly into the uterus. This is done around the time of your ovulation as it can cut down the time and distance the sperm cells have to travel, thereby increasing the chance of mating with an egg. Before the sperm cells are deposited, you may be put on fertility-enhancing drugs to spur ovulation. Semen is taken from your partner or donor. The doctor places the sperm right into your uterus. Conception takes place if the sperm is able to fertilize an egg and subsequently if the fertilized egg implants in the lining of your uterus.
Compared to other fertility treatments, it is simple and less complicated. It can make a sea change in your chances of conceiving a child, though it is highly subjective.
Why is intrauterine insemination carried out?
As you may be aware, a person’s ability to become pregnant depends on a variety of factors.
Cause of infertility cannot be explained: If no particular cause for infertility is identified, intrauterine insemination is considered the first-line of treatment along with ovulation-stimulating drugs.
Infertility related to endometriosis: If endometriosis is the cause of infertility, as a primary option intrauterine insemination is carried out along with medications to obtain good-quality egg.
Infertility due to male factor: One of the first steps in assessing infertility is analyzing your partner’s sperm, which may show that the sperm concentration is below par or movement of the sperm is weak or there are abnormalities in the shape and size of the sperm. With intrauterine insemination, some of these issues can be bypassed as only highly motile sperm is taken for this purpose.
Infertility related to cervical factor: Your cervix is situated at the lower end of the uterus, which is the opening between your vagina and uterus. Sperm is able to swim from vagina to the fallopian tube only if there is an ideal environment for it, which is ideally created by the mucus produced by the cervix during the time of ovulation. However, if the mucus in the cervix is very thick, it can impair the journey of the sperm, thereby preventing the sperm reaching the egg. Cervical scarring due to biopsy or other procedures can cause the mucous to be thick. As intrauterine insemination implants sperm directly into the uterus it can bypass cervix. This way there is an enhanced sperm availability to mate the egg.
Infertility related to ovulation: If the cause of infertility is related to problems related to ovulation, which may include anovulation (complete absence of ovulation) or reduced ovulation, intrauterine insemination is considered.
Allergic to semen: Seldom, a woman can be allergic to proteins contained in her partner’s semen, which may lead to redness, burning and welling where the semen comes in contact with the skin. Though through the use of a condom this issue can be overcome, it also prevents pregnancy. Intrauterine insemination is considered if the sensitivity is severe as many of the semen proteins are filtered out before injecting it into the uterus.
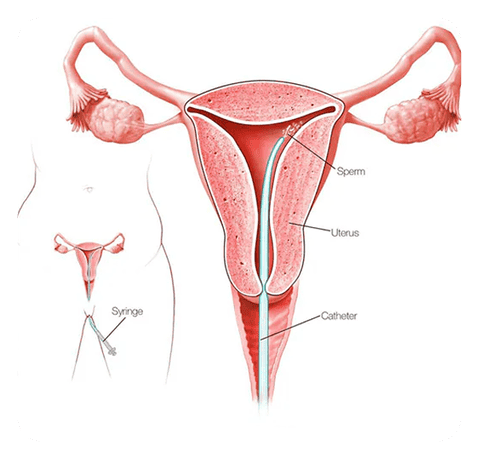
What happens during intrauterine insemination (IUI)?
Before doing the actual procedure, you will be evaluated for hormonal imbalance, infection and any structural issues. If you are a right candidate for the procedure, then you may be put on a range of fertility-boosting medications that will help make your egg mature and ready to be fertilized. If ovulation-stimulating drugs are used, careful monitoring is required. Blood tests and ultrasound scans from around six months of woman’s cycle will be performed as part of the monitoring process. These tests results will throw light on the maturation of eggs. As the time of implanting the sperm is very crucial, doctors monitor of signs of ovulation. It occurs generally once in every menstrual cycle when an ovary releases an egg due to hormonal changes. Your doctor or your health care specialist may have clear plan as to the timing of the procedure and what to expect out of it.
In order to avoid the risk of infection, doctors use only sterile instruments for the procedure. To do insemination at the nick of time, the help of an at-home urine ovulation predictor kit or an imaging method that lets your doctor visualize ovaries and eggs is sought; this imaging technique is called transvaginal ultrasound. Generally insemination is done after one or two days of detecting ovulation. Meanwhile, your partner or donor gives the semen sample at the doctor’s office. In some cases a vial of frozen sperm can be thawed before it is prepared for the procedure. As the non-sperm elements in the semen can cause reactions in the woman’s body, the sperm thus collected undergoes a procedure called “sperm washing” which separates a concentration of healthy sperm. However, if you are seeking the service of a sperm bank, the sperm thus being sent to the doctor’s clinic is already washed and ready for insemination. Administering a small and highly concentrated sample of active sperm increases the chances of achieving pregnancy. Some fertility clinics perform a second insemination the following day. Some clinics also prescribe progesterone to take after the procedure and through the initial stages of pregnancy if pregnancy is achieved.
If you are currently undergoing fertility-boosting medications for intrauterine insemination and experience any of the below-mentioned symptoms, you should call your doctor right away.
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- suddenly putting on weight
- experiencing shortness of breath
- nausea and vomiting
- severe and prolonged abdominal or pelvic pain
- sudden increase in waistline
Your visit to doctor’s clinic to have intrauterine insemination may take 15 to 20 minutes and the time taken for the procedure is just a minute or two with minimal discomfort. No medications or pain relievers are needed to carry out the procedure. It is generally carried out by a doctor or nurse who had special training in the procedure.
Careful coordination is something that is of utmost importance for the success of this procedure. In order to perform the procedure, you are supposed to lie down on the exam table and put your legs into the stirrups. It is carried out by sliding a speculum through your cervix into your uterus, parallels can be drawn here with a Pap test. The vial containing the sample of donor sperm is attached to the end of catheter. With the help of the catheter, the sperm is then inserted into the uterus directly through the cervical opening. This method maximizes the number of healthy sperm cells reaching the uterus. Upon the sperm mating an egg, pregnancy happens, the fertilized egg is then implanted in the lining of your uterus. It is done fast and anesthesia is not needed. It is a painless procedure, though some people may experience mild cramping. On completing the procedure, catheter is removed, followed by the speculum.
Post procedure:
After the procedure, you will be asked to lie on your back for a short period. Thereafter, you can get dressed and proceed with your normal daily activities. You may find a light spotting for a day or two after sperm insemination. Post procedure, the woman who had the test has to watch out for signs and symptoms of pregnancy. After about two weeks, you can do an at-home pregnancy test. However, testing too soon can produce a result that is either false-negative or false-positive.
False-negative: If the pregnancy hormones have not yet risen to the measurable volume, the test may show a negative result, when in fact you really are carrying.
False-positive: If you are on ovulation-boosting medications like hCG, as the medication is still in your blood stream may indicate a positive result, when in fact you are not pregnant.
Your doctors may ask you to come for a follow up visit about two weeks after an at-home pregnancy test for a blood test, which is more accurate in detecting pregnancy hormones after sperm insemination. In the unlikely event, if you are not yet pregnant, you can go in for a second round of sperm insemination before moving on to other fertility treatments. In order to maximize the chances of a positive result, the same treatment is often repeated for three to six months.
Success rate of intrauterine insemination:
Success rate in IUI Treatment in Trivandrum, kerala is quite high, second only to in-vitro fertilization (IVF). The likelihood of getting pregnant depends on a variety of factors. If a woman is undergoing sperm insemination every month, success rate may reach as high as 20% per cycle, though there are a lot of factors are at play here like age of the lady, type of infertility, whether ovulation-boosting drugs are used etc. Success rate of IUI is higher in women who are below the age of 40. However, the graph of success rate tends to come down if the woman is not getting pregnant after three cycles of intrauterine insemination.
However, intrauterine insemination is not recommended for the following patients:
- Women who are suffering from fallopian tubes diseases
- Women who had pelvic infections in the past
- Women with moderate to severe endometriosis
To conclude, intrauterine insemination is a comparatively less risky treatment that can be a wonderful option for couples who are experiencing infertility. In the unlikely event, if you are facing difficulty conceiving or have doubts about the options of fertility treatment, consult your gynecologist or a fertility specialist. Your doctor is the right person to suggest the accurate treatment to achieve pregnancy and intrauterine insemination can be an effective one.
For enquiries related to IUI Treatment in Kerala, send a message to www.kjkhospital.com/contact

