ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
From fertilization to delivery, pregnancy involves a number of stages in a woman’s body. One of the stages is the egg that is being fertilized travels to the uterus to attach itself. As for ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg does not reach uterus, instead it gets attached to the cervix, abdominal cavity or fallopian tube. According to medical studies, 1 out of every 50 pregnancies is ectopic.
If proper medical care is not sought an ectopic pregnancy can snowball into a medical emergency. Timely treatment brings down your risk of complications arising out of ectopic pregnancy and increases your chances of future normal pregnancies. Moreover, further health complications can also be averted by seeking proper medical treatment.
HOW DOES AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY OCCUR?
It is not always clear what causes an ectopic pregnancy. The following conditions have been linked to ectopic pregnancy:
- scarring and inflammation of the fallopian tube owing to previous surgery, infection or a disease condition
- factors related to hormonal changes
- genetic abnormalities
- disease conditions that impair and weaken fallopian tubes and reproductive organs
Remember, a doctor is always the right person to give you more accurate information about your health condition.
WHO ARE AT RISK OF DEVELOPING ECTOPIC PREGNANCY?
Generally it can be said that all sexually active women are at risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy. Risk factor goes up with any of the following:
- if the maternal age is 35 years or older
- if the lady had multiple abortions, pelvic surgery or abdominal surgery
- history of PID (pelvic inflammatory disease)
- if the pregnancy occurred in spite of IUD (intrauterine device) or tubal ligation
- if the pregnancy is enhanced by any procedures or fertility-inducting drugs
- if the lady has the history of STD (sexually transmitted diseases)
- if the fallopian tube has some structural abnormalities that make the passage of egg difficult
You should consult your doctor if you have any of the above risk factors. A doctor or a fertility specialist can give you guidelines to minimise the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy in the future.
SYMPTOMS TO LOOK OUT FOR
Soreness in the breast and tendency to vomit are common symptoms in both uterine and ectopic pregnancies, but the following symptoms are more prevalent in ectopic pregnancy and should seek a professional opinion:
- sharp spasms of pain in neck, shoulder, abdomen or pelvis
- severe pain on one side of the abdomen
- vaginal spotting or bleeding (light or heavy)
- fainting or dizziness
- rectal pressure
Contact your doctor if you experience any of the above-mentioned symptoms
HOW AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY IS DIAGNOSED
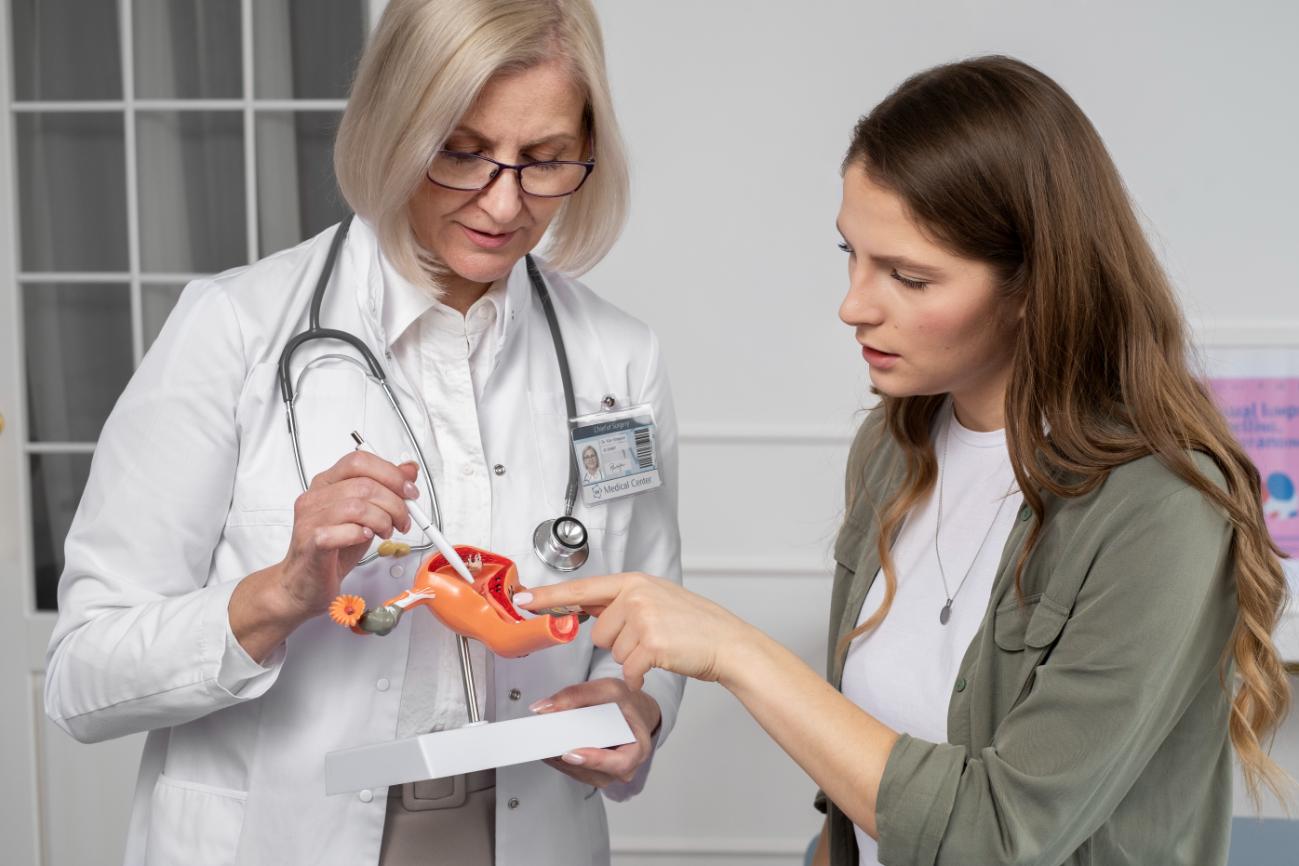
Unfortunately, an ectopic pregnancy cannot be diagnosed on physical examination though your doctor may perform one to rule out other risk factors. Your doctor may suggest you to undergo a transvaginal ultrasound. A special wand-like instrument is inserted into your vagina, with the help of this instrument your doctor will be able to observe your uterus thoroughly and look for a gestational sac.
In order to check your progesterone and hCG, your doctor may do blood tests of yours. These are pregnancy-related hormones. If the levels of these hormones are either decreasing or more or less the same, coupled with no gestational sac in the uterus, the pregnancy is likely to be ectopic.
If you suffer from intolerable bleeding or pain, there may not be sufficient time to perform all these. Moreover, in some extreme cases, fallopian tube could rupture, leading to significant internal bleeding, then doing an emergency surgery is the only way to save the life of the mother.
TREATMENT OF ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
As you know, ectopic pregnancy puts the health of the mother in a hazardous state. Furthermore, embryo will not be able to grow properly. It is important to take the embryo out for the mother’s immediate health and keep the mother fertile. Development of ectopic pregnancy and its location influence the treatment modalities.
DRUG TREATMENT
If your doctor finds that the ectopic pregnancy does not pose any immediate medical complications you may be prescribed medications that would prevent the ectopic mass from bursting. One common medication is methotrexate.
Methotrexate is a medication that arrests the growth of rapidly dividing cells, in this case ectopic cells. It is generally given in the form of an injection. When effective, this medication is likely to trigger symptoms that are similar to that of an abortion (passage of tissue, bleeding, cramping etc.). If this occurs further surgery can be averted. Methotrexate does not carry the risks of damaging the fallopian tube as against an operation. However, you will not be able to conceive for several months after taking this treatment.
SURGERY
Many surgeons may advise to undergo an operation to take out the embryo and repairing any internal damage. In order to see the internal organs properly during an operative procedure they insert a small camera through a small incision. The surgeons then remove the embryo and repair the fallopian tube if there is damage.
In the unlikely event, if the surgery does not produce the desired result, again a camera may be inserted, but this time through a larger incision. If the fallopian tube is damaged beyond repairs, it will also be removed.
POSTOPERATIVE CARE
You will be properly advised as to the care of your incisions after surgery. It is of prime importance to keep the wounds clean and dry while they heal. Check if there are any signs of infection like swelling, redness, hot to touch, foul-smelling drainage from the wound, excessive bleeding etc.
However, it is only natural to have light vaginal bleeding and small blood clots after the surgery. You can expect it to happen upto six weeks post surgery.
A complete bed rest is needed in the first week after the surgery and increase activity as tolerated in the following weeks. You are not supposed to lift anything heavier than 10 pounds during the resting phase. In order to avoid constipation drink plenty of fluid, refrain from sexual intercourse to give your pelvis proper rest.
If you feel pain or something is wrong, it is always better to contact your doctor.
PREVENTING ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
There is no fool-proof method to prevent or predict ectopic pregnancy though you can minimise the risk of developing ectopic pregnancy by maintaining good reproductive health. Using a condom while having sex brings down the risk of developing sexually transmitted diseases which can cause pelvic inflammatory disease – a condition that makes the fallopian tubes swollen. Kicking out the habit of smoking is also a good prevention strategy. As they say, it is better safe than sorry.
For any queries related to Ectopic Pregnancy, Connect with us