With new developments in the screening methods, it is now possible to detect risks for genetic mutations and chromosomal abnormalities in fetuses at very early stages.
First Trimester Screening is a comparatively new evaluation option that combines a maternal blood test and nuchal translucency ultrasound to identify risk for specific chromosomal abnormalities and fetal defects. This screening test is non-invasive and is done between 11 and 13 weeks of pregnancy and carries no risk to mother or baby. The blood sample is analyzed for the chemicals – free Beta hCG(human chorionic gonadotropin) and PAPP-A(pregnancy associated plasma protein-A) which are normally found in the blood of all pregnant women. The results from these blood samples help in determining risks for certain chromosomal abnormalities including Trisomy-21(Down’s Syndrome), Trisomy-18(Edward Syndrome) and Trisomy-13(Patau Syndrome). The nuchal translucency test which measures the skin on the back of baby’s neck help determine risks for certain types of birth defects like cardiac disorders.
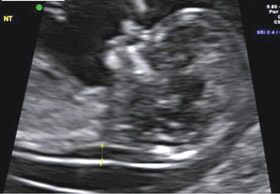
An ultrasound scan image showing the area at the back of baby’s neck (Nuchal Translucency)
An area that has been explored in recent years has been in isolating fetal genetic material present in maternal blood as a target for prenatal diagnosis. Cell free fetal DNA is the DNA which circulates freely in maternal blood. Analysis of cell free fetal DNA is another new option of first trimester screening generally opted for pregnant women of advanced maternal age.
It is important to understand that First Trimester Screening does not give definitive answers, they only indicate the possibility of a chromosomal defect or a birth defect which needs to be further evaluated using a series of tests and discussions. Also, these screening tests does not only consider the blood and ultrasound results, they also factor in the women’s age, weight, smoking status, past pregnancies etc.
If the screening test is positive, the couple would be offered diagnostic tests such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis which are almost 100% accurate in detecting chromosomal abnormalities. It is rare to have false positives or false negatives. These diagnostic tests are invasive and involves a minute risk of miscarriages and infections.
If the test result is negative, does not necessarily mean the baby will not have any abnormalities. Although the test helps in detecting the possibility of abnormalities, it does not guarantee a normal baby if the test is negative.
Around 95% of pregnant women who undergo the First Trimester Screening Test will be given a ‘low risk’ result.
Benefits of First Trimester Screening
Informing the parents about potential problems during pregnancy is part of good antenatal care. Early detection of a fetal condition gives parents the option of either terminating the pregnancy or preparing themselves to give best care to the affected child. It also prepares them for seeking further information, counselling and support. Babies with chromosomal abnormalities may require monitoring before birth for certain abnormalities like cardiac problems etc. Birth of such babies will also need specialized care.
For information regarding First Trimester or other screenings during pregnancy, or for booking for a Prenatal Screening, call 9447452568/041-2544080/2544706 or write to www.KJKHospital.com/contact