After having a tubal ligation, which is a permanent form of contraception, due to unforeseen circumstances, some women may seek a reversal of sterilization. Laparoscopic tubal recanalization, being a minimally invasive surgery, introduced a new dimension for tubal reconstruction. Within a short span of time laparoscopic tubal recanalization has emerged as an alternative route to perform microsurgical reversal of a ligated fallopian tube. The procedure aims at reconnecting the previously cut portions of the fallopian tube. After family planning some women want to reverse the procedure, which created a break in the fallopian tube. The reverse procedure involves reconnecting the fallopian tubes in order to become fertile again.
What are fallopian tubes?
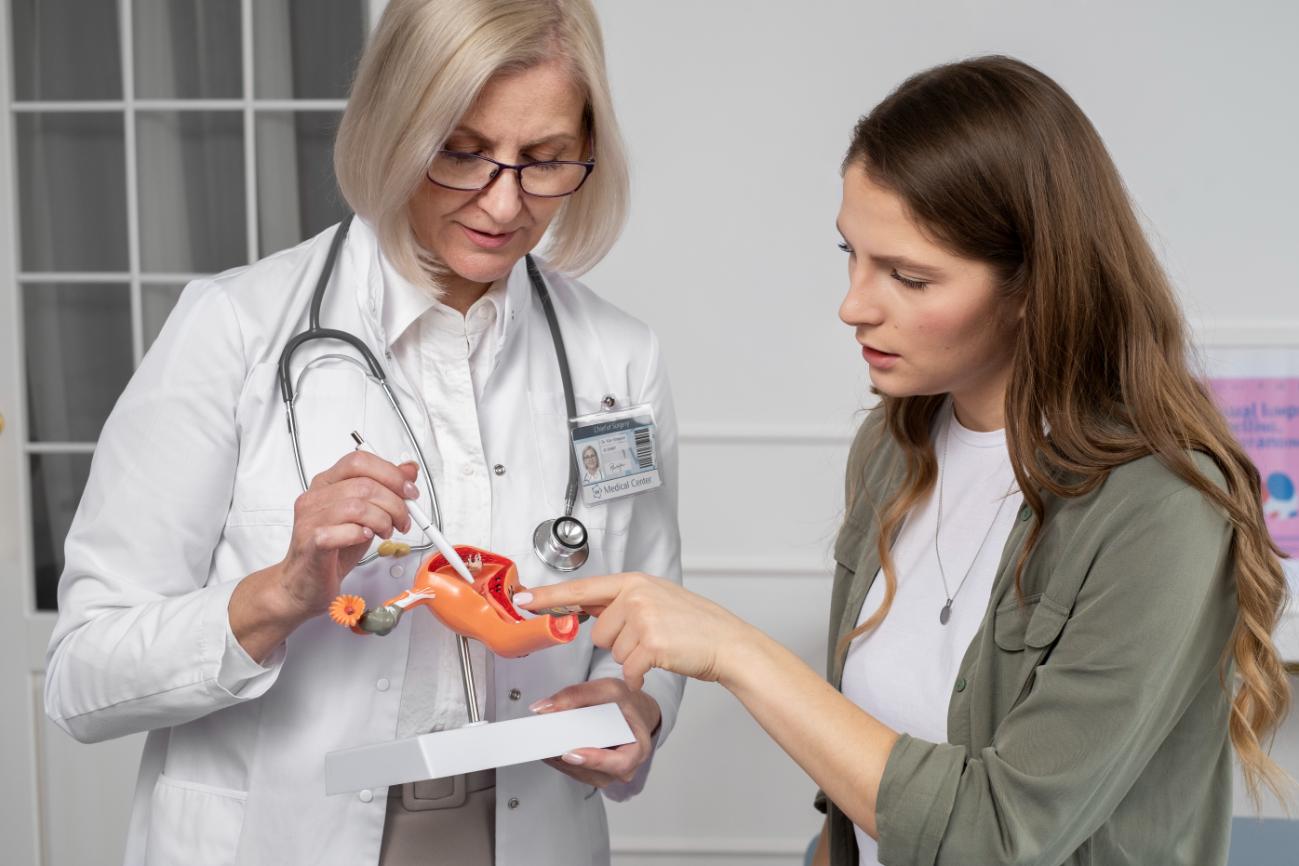
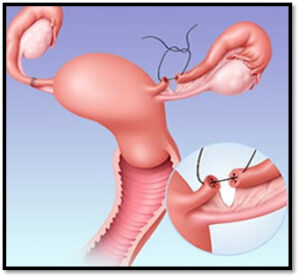
Fallopian tubes are an integral part of female fertility. Fallopian tubes are fine little tubular structures that connect the uterus to the ovary. Fallopian tubes provide passage for the eggs to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. During conception process, the ovary releases an egg, which travels into the fallopian tube, sperm travels into the fallopian tubes to fertilize the egg, thus an embryo is formed and it is nourished and transported to the uterus where the next stage of pregnancy takes place. Thus a block or cut in these tubes makes fertilization impossible.
Laparoscope and laparoscopy:
A slender tool with a video camera and light on the end. It is inserted through a small cut into your body. It provides live images of your internal organs so that surgeon can look at a video monitor and see what is happening. The magnification obtained is similar to that of obtained with an operating microscope. Without a laparoscope, surgeons would have to make a much larger opening. With a laparoscope, there is no need for the surgeon to reach into your body, which means less cutting. This process is called laparoscopy and it is a minimally invasive surgery.
What is laparoscopic tubal recanalization?
Tubal ligation is tying of the fallopian tube which will result in permanent contraception. However, the procedure can be reversed laparoscopically. It should be noted that the chances of women getting pregnant after re-canalization depends on age and the function of their ovaries. This is a sophisticated procedure, handled by just a few highly skilled surgeons.
Before the procedure:
The patient will be thoroughly examined and investigated before the procedure. Husband and wife will be briefed in a detailed way regarding the procedure. The procedure will be performed only if the fallopian tubes are suitable for reanastomosis and if there is adequate tube length.
During the procedure:
General anesthesia is the preferred choice of anesthesia for laparoscopic tubal recanalization. The procedure begins with making a small incision in or below the tummy button, about half an inch long. Once the incision is made, a harmless carbon dioxide gas is injected into your abdomen. This is done to raise the abdominal walls off your pelvic organs. This provides the surgeon an unobstructed view and a space to work upon. Then a laparoscope is inserted through the cut made to view the fallopian tubes. The already tied tubes are first untied and the two ends are then reattached thus allowing for the eggs to be fertilized once more.
The important factors determining the success of recanalization are technique of sterilization and the remaining length of the tube after recanalization. On completion of the procedure, laparoscope is taken out and the incisions are closed with stitches.
Recovery post procedure:
Once the procedure is over, you will be kept in the postoperative ward so that surgeons can observe you for any potential complications. You will be given a set of instructions as to how to take care of your body in general and the wound in particular during the recovery phase. Women can generally resume their activities of daily life and work life three days after the procedure.
The following are the common guidelines to be followed post surgery.
- There is no restriction on bathing or showering post procedure
- Bandages (Steri-Strips) can be removed after three days post procedure
- There is no restriction on sex one week post procedure
- It is normal to have vaginal bleeding for a few days after the procedure
- Periods will normally return after four to six weeks after the procedure
- The first two or three menstrual cycles may be a bit painful, coupled with heavier bleeding and discomfort
It is common to have some pain post procedure. Surgeon will instruct as to which medications can be taken to ameliorate the pain. There may a mild swelling in your abdomen, which will go away in a couple of days. There may be a general discomfort that lasts a few days such as:
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Abdominal cramps
- Gassy or bloated feeling
- Sore throat (from the breathing tube if general anesthesia was used)
Advantages of laparoscopic tubal recanalization:
Laparoscopic tubal recanalization has many advantages over open operation. The principal advantage of laparoscopic tubal recanalization is no big cut is made on the skin, which would result in minimal scarring. The procedure requires only minimal tissue handling, so less postoperative adhesions. The smaller incisions will also aid speedy recovery post surgery. Scope of complications is kept minimal. In most cases, patients will be able to leave the hospital post procedure within hours after having the procedure.