Ovarian cysts are small fluid-filled sacs that develop in a woman’s ovaries. Most cysts are harmless and remain without any symptoms, but some may cause complications like rupture, bleeding or pain. Most of the small ovarian cysts occur naturally and disappear in a few months without any treatment.
To understand ovarian cysts, it is important to understand the function of ovaries.
Ovaries and their function
Ovaries are two small bean shaped reproductive organs located on each side of the uterus. Every month during the middle of women’s menstrual cycle, ovary releases egg and this is called ovulation. While the egg grows inside the ovary, the estrogen is released which prepares the uterus for a developing pregnancy. The lining of uterus grows and thickens thus preparing for implantation of the fertilized egg. If the egg is not fertilized, the contents of the uterus breaks down and are expelled thus resulting in the onset of menstruation. This cycle occurs every month.
Who gets ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts are very common and are seen in women of all ages. It is said that about 70% of women develop ovarian cysts at least once in their lifetime. In most of the cases, these cysts are benign harmless and does not show any symptom.
Causes and risk factors
There is no defined cause of ovarian cysts however some hormonal and endometrial causes have been indicated. Certain risk factors have been identified which causes these cysts. Risk factors include:
- History of previous ovarian cysts
- Obesity
- Infertility
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Early menstruation (before 11 years of age)
- Hypothyroidism
Symptoms of ovarian cysts
Most ovarian cysts are small and does not cause any symptom. In fact, many women remain unaware that they have ovarian cysts. Some cysts cause symptoms such as:
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Irregular menstruation
- Uterine bleeding
- Bloating or fullness in the abdomen
- Pain or pressure with urination or bowel movement
- Pain during intercourse
- Unexplained Weight gain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain during menstruation
- Problems with control of urination
Types of ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts are broadly classified into two types – Functional and Non-Functional (Pathological). Functional ovarian cysts are the most common ones and develop as part of the menstrual cycle. They are harmless and generally disappear on their own. Non-functional ovarian cysts form because of abnormal cell growth.
There are several types of functional and non-functional ovarian cysts. Some cysts are related to ovulation like the follicular cysts or corpus luteum cysts. Other types include Dermoid cyst, endometrioid cysts, Polycystic ovaries, Cystadenoma and then there are the cancerous ones – Ovarian cancers.
Ovarian cysts are less common post menopause. Postmenopausal women with ovarian cysts are at higher risk for ovarian cancer
Also Read: Ovarian Cyst And Pregnancy: Could An Ovarian Cyst Cause Infertility
Treatment for ovarian cysts
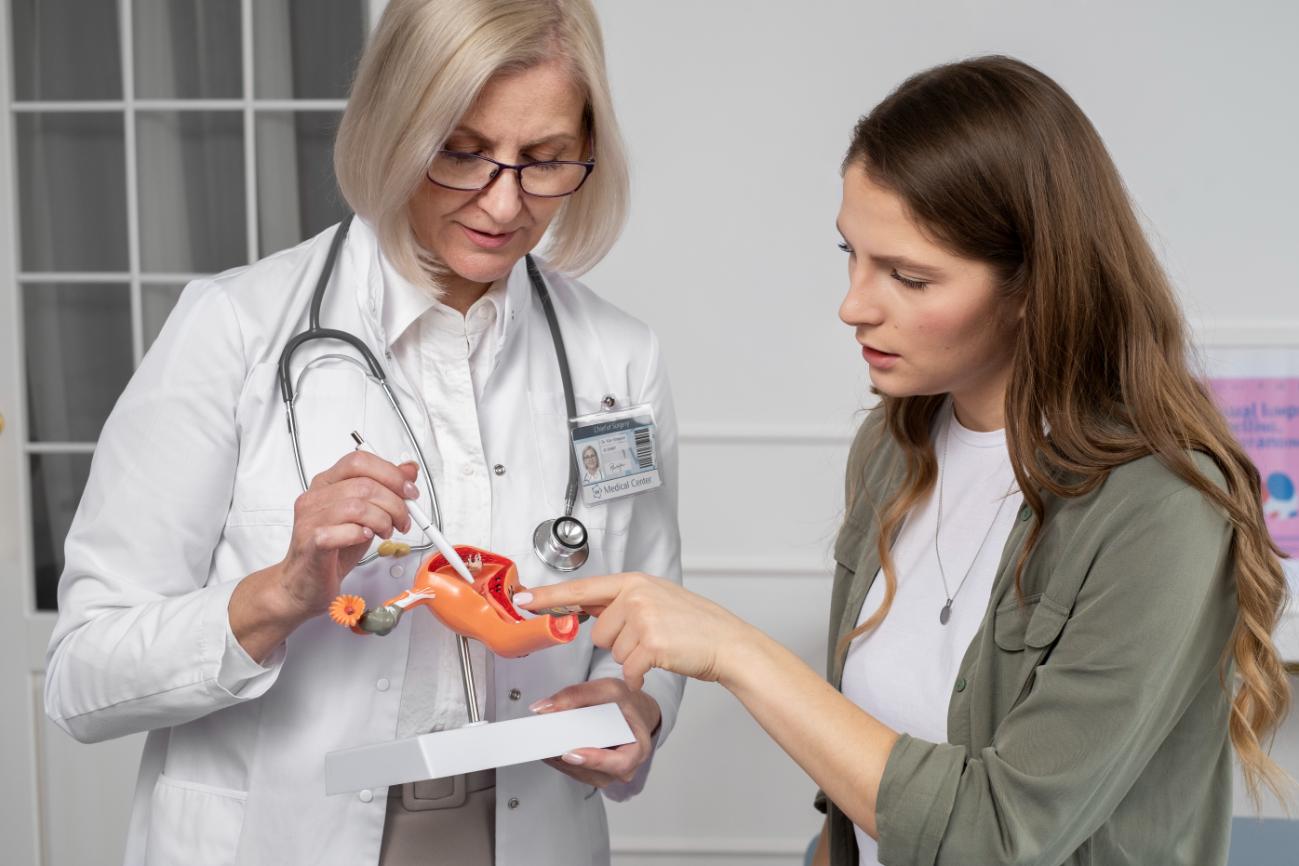
Ovarian cysts are usually diagnosed by one or more of the following methods:
Pelvic exam
Ultrasound
CT Scan
MRI
Blood Test
Hormone level tests
Small functional cysts which does not cause any symptom are left untreated with observation over time. For cysts (generally larger ones) that cause pain, paracetamol or ibuprofen may be used. People with frequent occurrence of cysts are advised to take hormonal birth control pills which helps in preventing further cysts. Cysts that are persistent and get larger over time, appear non-functional, cause pain and discomfort may be removed by surgery. Two types of surgeries are done. Laparoscopy for smaller functional cysts and Laparotomy for larger cysts and sometimes cancerous ones. Ovarian cancers may also be treated using chemotherapy and radiation.
Complications associated with ovarian cysts
Complications from ovarian cysts are rare however in certain cases it causes complications which includes:
Ovarian Torsion where the cyst can cause painful twisting of ovary.
Rupture of Cyst can cause severe pain and internal bleeding
For questions related to ovarian cysts, their diagnosis and treatment options, drop a message here – www.KJKHospital.com/contact or call for an appointment – 9447452568/0471-2544080